HEPA filter made of PTFE(polytetrafluoroethylene) as filter material is called PTFE HEPA filter.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a high-efficiency air filter material, has been widely used in clean rooms in the electronics industry due to its advantages of high filtration efficiency, low initial resistance, and no boron release.
Research shows that PTFE is essentially a fiber filter material, with an average fiber diameter of 60-85nm, which is much lower than the 668.8nm of glass fiber filter material; the filtration efficiency of high-efficiency PTFE is equivalent to that of glass fiber filter material, and its initial resistance Less than 50% of glass fiber filter material.
General introduction to PTFE
The American DuPont Company first produced PTFE through uniaxial stretching in the 1960s. However, due to its dense structure, this uniaxially stretched film can only be used in the sealing field.
In 1976, the American Gore Company used a bidirectional mechanical stretching method to prepare an expanded PTFE microporous filter material and applied it to industrial dust removal for the first time.

After that, companies such as Pall, Millipore, and Donaldson in the United States and Nitto Denko and Daikin in Japan successfully developed PTFE filtration materials.
Over the past few decades, with process technology’s continuous upgrading and improvement, PTFE has developed into a new filter material with a filtration efficiency comparable to ultra-fine glass fiber filter materials and an absolute advantage in filtration resistance. In high-efficiency air filtration, occupies an essential position in applications.
What is the structure and performance of PTFE material?
The primary performance of the HEPA filter comes from its filter material, so that I will focus on the structure and performance of the PTFE material here.
PTFE filter material morphology and structure
Observe the morphology of PTFE and ultrafine glass fiber filter materials using a scanning electron microscope, and it can be seen that, similar to the structure of ultra-fine glass fiber filter material, PTFE filter material is also composed of a variety of randomly arranged fibers of different fineness.

Among them, the alternation between thicker and thinner fibers causes the fibers in the filter material to form an obvious “bulge” structure, which effectively regulates the distance between fibers, thus achieving the adjustment of fiber filling density.
This is one of the essential reasons why PTFE filter material has excellent capture ability and low filtration resistance for fine particles.
Fiber diameter distribution
PTFE filter materials comprise a series of fibers with different diameters and contents. The fiber diameters are distributed between 10 and 240nm, much lower than the 50-2600nm of glass fiber filter materials.
The peak of the filter fiber diameter distribution curve is 45nm, and the number of fibers below 100nm accounts for 85.47%.

PTFE filter material has a narrow fiber diameter distribution, a denser filter material structure, and a higher content of fine fibers, which results in a more obvious interception and diffusion effect on fine particles and a better ability to capture fine particles.
The average diameter of PTFE fibers reaches the nanometer level, which is one of the essential reasons why PTFE has low resistance and high efficiency.
Filtration efficiency and MPPs(most penetrating particle size)
When testing with DOP, as the particle size of DOP particles increases, the filtration efficiency of ultrafine glass fiber and PTFE HEPA filters shows a noticeable trend of first decreasing and then increasing; that is, there is a minimum efficiency point at a certain point between 0.02 and 0.30 μm. This point is called the most penetrating particle size (MPPS), which indicates that the filtration of particulate matter by both types of filter media is not a single screening mechanism.
Among them, the MPPS of the PTFE HEPA filter is about 0.060μm-0.075μm, which is lower than the 0.12μm of ultra-fine glass fiber HEPA filter.

This characteristic of the air filter material is because the filtration mechanism of the filter material for particulate matter is related to the filter material’s fiber diameter and the particulate matter’s size.
Regarding fiber filter media, the filtration of particles below 0.1μm is mainly based on the Brownian diffusion effect.
As the particle size increases, the diffusion effect gradually weakens, and the interception and inertial collision effects gradually increase. In this way, there must be a point where the filtration efficiency of the filter material is the lowest.
At the same time, the average fiber diameter of the PTFE is much lower than that of ultra-fine glass fiber, reaching the nanometer scale, which significantly enhances the adhesion of PTFE fiber to fine particles, that is, the van der Waals force.
Moreover, the random accumulation of nanofibers greatly enhances the interception effect of the filter material on particulate matter, resulting in the MPPS of the PTFE HEPA filter being smaller than that of the glass fiber HEPA filter.
PTFE filter resistance
Compared with ultra-fine glass fiber HEPA filters, the PTFE HEPA filter has obvious resistance advantages. Taking the test air volume of 32L/min as an example, the filtration resistance of glass fiber filter material is 300.8Pa, and the resistance of PTFE filter material is 147.65Pa, which is glass 49.09% of the resistance of fiber filter material.
As the test wind speed increases, the PTFE HEPA filter’s resistance increases slower than the glass fiber filter material, which is related to the fact that the PTFE membrane has a smaller fiber diameter than the glass fiber filter material.
The filtration resistance comes from the drag force of the fibers on the airflow. The PTFE filter material has low resistance, which is related to the airflow’s slip effect near the nanofibers. The degree of air slippage near a single fiber can be calculated based on the Knudsen number Kn. The formula is:

In the formula, λ is the mean free path of air molecules, and its value is 65.3nm at normal temperature and pressure; d is the fiber diameter, nm.
When the fiber diameter d<13nm, the sliding effect of gas near the fiber is very severe, and the drag force of the fiber on the airflow can be basically ignored.
The fiber diameter of PTFE filter material is between 10 and 240nm. The flow of air around the fiber is in the free molecular and transitional flow states, which makes the slip effect of airflow on the surface of PTFE fiber much higher than that of glass fiber, resulting in a minor filtration resistance of the PTFE filter material.

At the same time, as Kn increases, the rarefaction effect becomes significant for the microflow of air, which can effectively reduce the effective viscosity of the air in a low flow state, thereby reducing frictional resistance. This is also one of the reasons why the PTFE HEPA filter has low filtration resistance.
Dust holding capacity
Dust holding capacity refers to the total mass of dust particles captured by the air filter material per unit area when the filter resistance reaches a specific value. It is an important parameter to measure the service life of the HEPA filter.
It has a decisive impact on the cost of HEPA filters in actual operation.
Although the initial resistance of glass fiber filter material is higher than that of PTFE filter material, its resistance increases slowly during the dust-holding process.
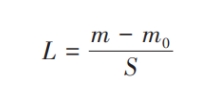
This is related to the fact that the average fiber diameter of glass fiber filter material is larger, and the pores between fibers are more developed than that of PTFE filter material.
Since the pore size of the PTFE filter material is small, its particulate matter filtration is mainly based on the interception effect. Pollutants are more likely to quickly form a dense filter cake layer on the PTFE surface, causing the filtration resistance to increase rapidly.
Therefore, compared with glass fiber HEPA filters, the dust-holding capacity of PTFE HEPA filters is smaller.
Last Summary
Compared with ultra-fine glass fiber HEPA filters, PTFE HEPA filters have the following significant advantages:
High filtration efficiency, up to U17 (99.999995%) level.
The filtration resistance is low, about 40% of that of ultra-fine glass fiber with the same filtration efficiency level.
It has good toughness and high mechanical strength, which overcomes the shortcomings of ultra-fine glass fiber, such as high brittleness and poor processing performance.
It has good high-temperature and corrosion resistance and can efficiently filtrate high-temperature smoke and corrosive gases. Based on this, PTFE filter material is recognized as one of the most promising high-efficiency air filtration materials.
At the same time, the dust-holding capacity of the PTFE HEPA filter is lower than that of glass fiber.
Further improving the dust-holding performance of PTFE filter material is the key to expanding its application in the air filtration industry in the future.






