As the final air filter for air treatment and filtration in clean rooms, the importance of HEPA filters is self-evident, especially in sterile production environments where HEPA air filters are mandatory.
I have written about how the air filter works in a previous article, so I will not introduce it in this article.
We all know that HEPA filters generally use fiber filter paper as filter material, so I mainly discuss the factors that affect the efficiency of fiber filter paper to understand what factors affect the filtration efficiency of HEPA filters.
Many factors affect the efficiency of fiber filter paper; the main ones are particle diameter, fiber thickness, filtration speed, filling rate, temperature, humidity, pressure, dust holding capacity, etc.
Let’s take a closer look at the details of each factor below.
Factor 1 Effect of particle properties
When HEPA filter filters polydisperse particles, both theoretical analysis and actual measurement results show that as the diameter of the particles increases from small to large, the overall filtration efficiency changes first and then increases. The reason is that various capture mechanisms have different effects on particles of different particle sizes.
Smaller particles are deposited due to diffusion, and larger particles are captured under interception and inertia. When the particle size increases from small to large, the diffusion effects gradually weaken, and the inertia and interception effects increase progressively.
This results in a weakening of the overall capture efficiency in the small particle size range.
The particle filtration efficiency becomes more vital in the large particle size range so that there is the lowest point in the filtration efficiency curve related to particle size; that is, there is a minimum efficiency value during the change process.
The particle size corresponding to this point is the most penetrable particle size(MPPS).
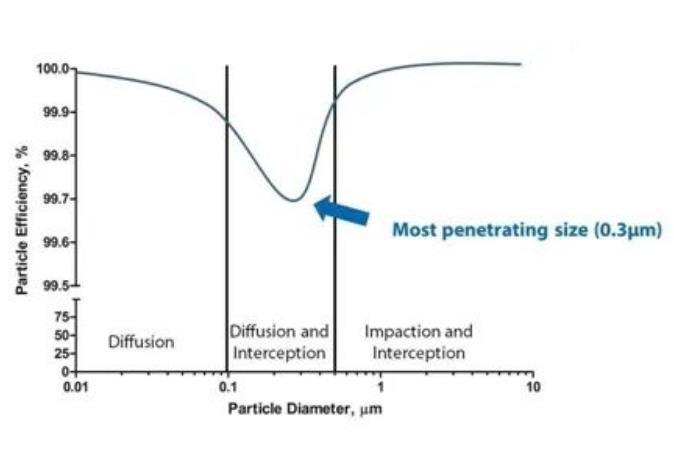
This particle size is not a fixed value. Many factors affect it. Different fibers and different filtration rates will cause its numerical value to change, and temperature will also cause the most easily penetrated particle size to mutate to a certain extent.
Even if the particle size is the same, particles in different phase states affect the filtration efficiency differently. Using fixed particle measurement can make the HEPA filter more efficient. Of course, this only happens during testing.
Factor 2 The influence of fiber thickness
When other parameters remain unchanged and only the fiber diameter changes, the filtration efficiency decreases as the fiber diameter increases.
This is because as the fiber diameter increases, the interception coefficient of the interception effect decreases accordingly, resulting in a decrease in the collection efficiency of the two related mechanisms, thus causing a reduction in the overall filtration efficiency.

This is why the fibers in the HEPA filter are much finer than those in medium-efficiency filter paper. Of course, the finer the fiber, the higher the resistance.
In addition, as the fiber diameter increases, the interception coefficient decreases, the inertial effect weakens, the most penetrable particle size(MPPS) gradually becomes larger, and the extreme point of the efficiency curve moves to the right.
Factor 3 Effect of filtration speed
When the filtration rate increases, the diffusion efficiency decreases, the inertial efficiency increases, and the interception efficiency increases. Therefore, the total efficiency first decreases and then increases. The maximum penetration particle size gradually decreases, and the extreme point of the efficiency curve moves to the left.
At the same time, as the filtration rate decreases, the filtration efficiency of the filter paper increases significantly.

The basic relationship is that if the filtration speed is doubled down, the filtration efficiency will be approximately increased by an order of magnitude.
This is because the reduction in filtration speed increases the time it takes for particles to pass through the HEPA filter paper, thereby increasing the probability of particles being captured, and therefore the filtration efficiency increases significantly.
When the filter paper adopts a filtration speed of 1cm/s, its transmittance is 100 times lower than the filtration speed of 5.3cm/s specified by the American standard. This also explains why the efficiency of the same grade filter paper varies greatly when tested in different countries.
Factor 4 Effect of fiber filling rate
As the fiber filling rate increases, the density of the fiber layer increases, and the inertial and interception efficiency increases. Although the diffusion effects decrease due to the increase in flow rate, the overall filtration efficiency is still improved.
However, it should be noted that the increase in resistance during this process is much faster than the increase in overall efficiency, so it is not a good idea to increase the fiber filling rate to improve the efficiency of the HEPA filter.
In this regard, I use another sentence to say that the greater the fiber density, the higher the filtration efficiency, but the greater the resistance.
Factor 5 Effect of airflow temperature
The increase in airflow temperature will increase the diffusion coefficient of particles, which increases the diffusion efficiency of sub-micron particles.
However, as the temperature increases, the viscosity of the gas increases, which reduces the deposition efficiency of large particles relying on gravity and inertial effects and increases the filtration resistance.
This change in efficiency will cause the most penetrating particle size to increase, causing the extreme point of the efficiency curve to move to the right, possibly causing the shape of the curve to change.
Factor 6 Effect of airflow humidity
As the airflow’s humidity increases, tiny particles’ penetration ability increases, resulting in a decrease in efficiency. The reason is that the moist air causes the electrostatic effect to disappear, Brownian motion weakens, and subsequent air flows easily entrain the particles and continue penetrating.
However, a liquid film will form on the fiber’s surface at high humidity. The contact area between the particles and the HEPA filter fiber will increase, causing the van der Waals force to grow and the rebound phenomenon to decrease—the filtration efficiency of large particles will increase.
Some studies believe the filtration efficiency will increase significantly for non-hygroscopic particles when humidity is high.
Of course, if the humidity is too high so that droplets appear on the HEPA filter material’s surface, it will decrease filtration efficiency.
Factor 7 Effect of air flow pressure
The reduction of airflow pressure will reduce the air density and increase the free path of air molecules, thereby increasing the sliding correction coefficient, the diffusion coefficient, and inertial parameters.
Therefore, diffusion and inertial effects are increased but have little impact on interception effects.
Last summary
Many factors affect the efficiency of HEPA filter paper. These factors have become issues to be considered when designing industrial clean rooms. Whether it is a medical hospital or the electronics industry, they cannot be ignored.






